Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations with fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to be given to infants? How can you lower the temperature in older children? What medications are the safest?
In this article:
The birth of a baby is a wonderful period in a woman’s life. But the joy of communicating with the baby can be overshadowed by some troubles. Young mothers note pain that occurs in the mammary glands. Many people have breast pain during breastfeeding, both before and after feeding.
According to the nature and duration, the pain can be nagging, piercing, short-term, constant and dull. To diagnose the pathology that caused the discomfort, you need to visit a gynecologist. A speedy recovery depends on timely contact with a specialist.
What is the cause of chest pain
In gynecology, there are several reasons why pain occurs. Some of them are associated with changes in the body after childbirth. Others are more dangerous pathologies and require specific treatment.
Physiological pain during breastfeeding includes:
- intense milk flow during feeding;
- improper latching of the breast by the child;
- production of oxytocin;
- feeding according to the schedule;
- hyperlactation.
Among the pathologies that cause pain are:
- lactostasis;
- mastitis;
- cracked nipples;
- cystic inflammation of the mammary gland;
- thoracic duct candidiasis;
- the presence of malignant tumors in the gland.
Symptoms of physiological pain in the mammary gland
If a woman experiences pain while breastfeeding, she needs to analyze the symptoms and identify the cause as soon as possible. In some cases, doctor intervention is not required.
Milk rush
If your breasts hurt during breastfeeding in the first weeks after childbirth, but there are no lumps or formations, this is a physiological process. During this period, there is an intense flow of milk to the glands. The pain is associated with the expansion of the gland ducts. Mothers notice that the child does not have time to swallow the milk that streams from the breast. After 1-2 minutes, everything falls into place: the pressure in the ducts drops, the baby sucks calmly, and the chest pain subsides.
Incorrect nipple latching
Many young mothers put their baby to the breast incorrectly. Such actions lead to cracks in the delicate skin of the nipples and compression of the ducts near the areola. As a result, nagging pain occurs during breastfeeding. To avoid this problem, the mother must ensure that the baby grasps the breast correctly. The baby's lips should be slightly turned out, and the nipple and areola should be captured in the baby's mouth.

Oxytocin production
In the first weeks after birth, the uterus returns to its normal size. Its rapid reduction is facilitated by the production of the hormone oxytocin. An intense release of the hormone occurs during breastfeeding. In this case, the woman experiences aching pain not only in the chest, but also in the lower abdomen. The discomfort will go away as soon as the uterus shrinks to the proper size. This usually happens 1 - 1.5 months after birth.
Feeding according to the schedule
Many pediatricians recommend adhering to a strict feeding regimen. As a rule, such actions lead to overflow of the thoracic ducts with milk and stagnation in the glands. The chest becomes stone-like and painful. Relief occurs when feeding or pumping.
Hyperlactation
All processes in the body are regulated by the brain. Since the body does not yet know how much milk is needed to satisfy the baby’s hunger, it tries to produce it in excess. Closer to 3 months of a child’s life, lactation will become mature and there will be the amount of milk that is necessary to meet the needs of the baby. Accordingly, the pain will disappear over time.
Symptoms of pathological pain during breastfeeding
You should be concerned if the mammary gland hurts during breastfeeding, and the discomfort is accompanied by:
- increased body temperature;
- aches, chills;
- redness of the breast;
- bloody discharge from the ducts;
- presence of lumps and lumps in the breast;
- an increase in size of one breast relative to the other.
Such symptoms indicate the presence of pathological foci of infection in the gland or neoplasms.
Lactostasis
This problem is most common in breastfeeding women. In simple words, this is a blockage of the milk ducts as a result of insufficient emptying of the breast. Occurs in the first month after birth. Intensive milk production leads to the fact that the baby does not empty the breast completely. The milk stagnates and bacteria multiply in the ducts, causing inflammation.
The disease progresses with lightning speed. Symptoms appear suddenly:
- a sharp rise in body temperature to 40° C;
- chest pain when touched and fed;
- redness of the affected gland;
- secretion of breast milk in drops;
- increase in size of the diseased breast.
With rational treatment, symptoms disappear after 3-4 days, and lactation returns to normal.
Mastitis
This is an inflammatory disease of the mammary glands, characterized by the development of an abscess. Milk is released from the breast mixed with pus and blood. For this pathology, surgical excision of the affected gland is indicated.
Mastitis occurs when:
- hypothermia;
- injury;
- penetration of infection into the gland through microtraumas on the nipple.
Mastitis may be a consequence of advanced lactostasis.
Cracked nipples
The problem occurs in the following cases:
- improper attachment of the baby to the breast;
- insufficient or excessive hygiene care;
- incorrectly selected bra;
- improper pumping (pressure on the nipple).
As a rule, with cracks, the mammary gland hurts during breastfeeding. The child's saliva irritates the delicate skin, which is accompanied by pain. Cracks are dangerous due to the penetration of infection through the affected skin, which leads to serious diseases such as mastitis and mammary candidiasis.
Candidiasis
With candidiasis (thrush), a woman experiences itching, burning and pain when feeding. Fungal infection and bacteria (staphylococci) penetrate the skin through cracks. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that a woman passes candidiasis to her child during feeding. It is more difficult to treat thrush in a baby. A fungal disease affects the baby's oral cavity. The result is refusal to breastfeed due to unpleasant sensations.
Cystic inflammation
Feeding may be accompanied by pain if there are benign formations in the woman’s breast - cysts. The size of the formation can range from several millimeters to tens of centimeters. The exact size of the cyst is diagnosed by ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. The formation causes pain and a feeling of fullness when feeding. This is due to the fact that blood vessels and milk ducts are compressed. A woman can detect a large cyst on her own. Lying on your back with your arm raised up, each area of the gland is examined by palpation. If lumps or lumps are detected, you should contact a gynecologist.
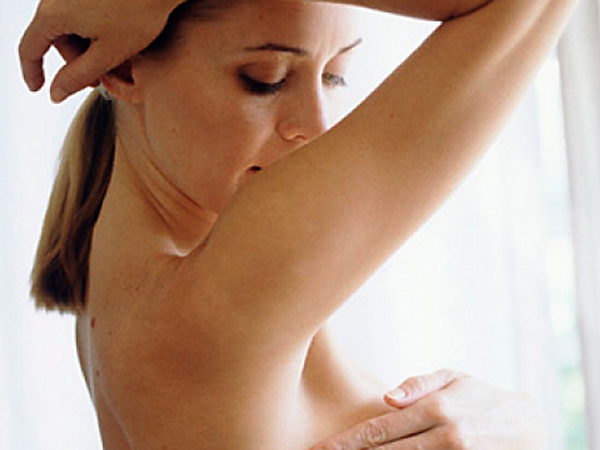

Breast cancer
If there is a malignant tumor, feeding causes pain, and blood is released from the glands. The main thing is not to panic. In the early stages, the disease can be successfully treated.
How to get rid of pain during breastfeeding
For physiological pain, no specific treatment is required. In due time, the body will return to normal, lactation will be established and the pain will go away. If the pain is caused by pathology of the mammary glands, you should immediately consult a specialist.
For lactostasis, treatment is indicated to eliminate milk stagnation and relieve inflammation. This includes:
- taking penicillin antibiotics;
- massage with camphor oil;
- warm shower;
- antipyretic drugs;
- Frequent pumping of the sore breast.
Mastitis requires surgery. The abscess is removed together with the affected gland. If purulent impurities are not observed in the milk, doctors prescribe conservative treatment, mainly antibiotics.
You can get rid of cracks using ointments containing panthenol and sea buckthorn oil. Regular breast care for a nursing woman is the best remedy for cracks.
Cysts in the breast require observation. With intensive growth, surgical treatment is indicated.
Candidiasis or thrush is treated with antifungal medications. As a rule, Candit or Clotrimazole ointment is prescribed.
When a woman is diagnosed with a malignant tumor, the oncologist prescribes rational treatment.
Preventive actions
To avoid breast problems during feeding, it is important to follow simple rules:
- Follow the rules of hygiene - take a shower 1-2 times a day.
- Inspect your nipples daily for microtrauma.
- Feed your baby on demand.
- Follow proper pumping technique.
- Correctly attach the baby to the breast.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Give your baby a second breast only after the first one has completely emptied.
- Regularly palpate your breasts for lumps.
- Be examined by specialists annually.
Pain during feeding can occur for various reasons. Even the most harmless cracks in the nipples can lead to the development of serious pathologies. It is better to consult a specialist once again and prevent possible diseases.
Breast milk is necessary for your baby to fully develop. No adapted formula can replace the value of mother's milk. Try to feed your child as long as possible, but do not forget about your own health.
Video on how to avoid cracked nipples



