Antipyretics for children are prescribed by a pediatrician. But there are emergency situations with fever when the child needs to be given medicine immediately. Then the parents take responsibility and use antipyretic drugs. What is allowed to be given to infants? How can you lower the temperature in older children? What medications are the safest?
Breastfeeding a baby can be painful for the mother. This happens when the nipples are cracked, milk flows in and it stagnates in the milk ducts. The sooner the cause is identified, the easier it will be to eliminate it.
Mother's milk is the best nutrition for a baby. When breastfeeding, mother and baby become closer under the influence of joint emotional satisfaction. But sometimes this feeling of closeness is overshadowed by pain in the mammary glands. By immediately identifying and eliminating the cause of concern, you can avoid long-term treatment and interruption of feeding
After childbirth, women's breasts are especially sensitive. The flow of milk is accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the mammary glands. Some heaviness, and sometimes tingling or tingling in them are natural signals that it is time to feed the baby. Initially causing discomfort, they reduce their intensity after a few days. But in the first week, hot flashes occur even during feeding, disturbing the young mother.
At this time, slight redness of the nipples is acceptable. Their sensitive skin rubs against the child’s gums and responds with a slight burning sensation. It should disappear after a few feedings. If this does not happen, then under no circumstances should you tolerate increasing pain. It means the appearance of cracks, which become gateways for infection. A nursing mother needs to learn how to properly attach the baby, making sure that it completely grasps both the nipple and the areola.
The described soreness in the mammary glands during feeding can be called natural and it is “treated” by regular feeding. After the menstrual cycle is restored, breast engorgement returns before menstruation. But there are other reasons why a nursing woman has breast pain:
- cracked nipples;
- lactostasis;
- mastitis;
- thrush and other infections;
- abrupt interruption of feeding.
In maternity and postpartum classes, nurses teach some relaxation techniques to help cope with hot flashes. They show how to hold a baby while feeding and wean him from the breast without damaging the skin of the nipple. At the same time, alarming symptoms during breastfeeding are highlighted.

Incorrect attachment
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW:Pain and crunching in the joints over time can lead to dire consequences - local or complete restriction of movement in the joint, even disability. People, taught by bitter experience, use a natural remedy recommended by Professor Bubnovsky to heal joints...
The mammary gland that the baby sucks must be supported from below by the mother's hand. The baby's chin must touch the breast, and the nipple, along with the areola, is in the mouth. In another case, the mother experiences pain during feeding, and the damaged skin hurts afterwards.
If correct attachment does not help, then the nursing mother should pay attention to the length of the child’s frenulum. The short frenulum stretches over time. But for overall health, it may be safer to cut it. This operation is performed by a pediatrician or dentist.
To avoid inflammation of microcracks and abrasions on the nipples, the mother must take care of her own hygiene. For this:
- after feeding, express the remaining milk and wash the breast;
- nipples are immediately lubricated with sea buckthorn oil or other healing preparations;
- dry the skin in the open air;
- exclude tight or uncomfortable bras;
- use breast pads and change them on time.
These simple treatments will help heal existing skin damage. If there are no diseases, the mammary glands are alternated at each feeding, after which they are cleaned and air baths are performed.
Thrush in mother and child
Sharp pain in the nipples of a nursing mother, burning and itching is one of the important symptoms of thrush. The activity of the Candida fungus can occur during feeding at any time. Occurring in the baby’s mouth, colonies of harmful microorganisms spread to the mother’s breast.
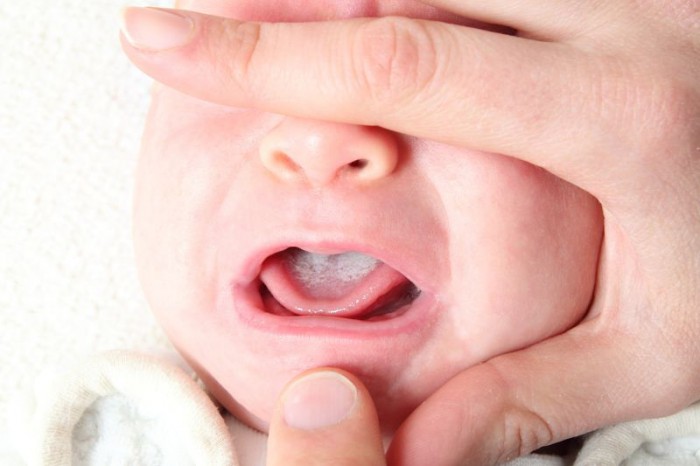
A whitish coating on the reddened mucous membranes of the oral cavity, and general restlessness of the baby are the first alarming signs of a fungal infection. Although it rarely affects the milk ducts, you should not put off visiting a doctor. The therapist prescribes treatment for two people at once.
Lactostasis
Over the course of three months, the mother's body gets used to the needs of the newborn. During this period, regularity and frequency are important in breastfeeding. At first, there may be less or more milk than the baby needs. Later, the production of the hormones prolactin and oxytocin, responsible for the amount of nutrient fluid, normalizes. It is the latter that prevents stagnation of milk in the mammary gland.
Oxytocin relaxes the milk ducts. Baby crying, caring and even thinking about the baby increases its production. And unnecessary anxiety interrupts the stable replenishment of the hormone. This is one of the reasons for lactostasis, but others can be identified:
- incomplete release of milk from the breast;
- hypothermia, bruise or injury to the mammary gland;
- cracked nipples;
- dehydration;
- pinching of the milk ducts due to improper feeding or underwear;
- refusal to breastfeed while lactation continues.
Feeding becomes painful, but after it you feel relief. The mammary gland, in which stagnation has occurred, swells, compactions are felt in it, the local temperature rises, and milk is sprayed unevenly or does not come out at all. This condition requires immediate response, as it can be complicated by mastitis.
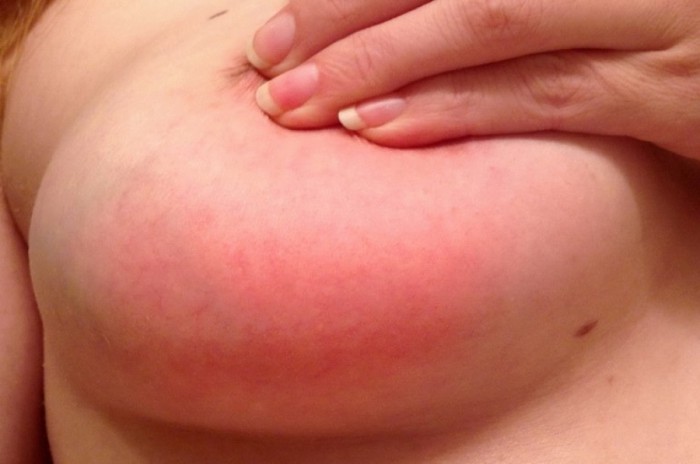
Mastitis and its difference from lactostasis
If milk retention in the milk ducts is not eliminated within 1-2 days, congestive mastitis develops, quickly turning into an infectious form. Mastitis is an inflammatory process caused by the coagulation of milk in the mammary ducts and alveoli. It occurs without previous stagnation if the mammary gland becomes infected through cracks in the nipples.
Early symptoms of mastitis are very similar to signs of lactostasis, but more pronounced. Complete differentiation is carried out using laboratory tests. But usually there are enough characteristic differences.
- Palpation. With lactostasis, palpating the lumps does not increase the pain, and the accumulated milk has clear boundaries. With mastitis, the resulting infiltrate blurs the contours of the inflammation, the breast hurts, swells and turns red.
- Milk secretion. Simple congestion is relieved by feeding from the diseased gland. Very painful pumping during inflammation does not bring relief - this is one of the important differences. Purulent discharge is possible.
- General state. Mastitis is characterized by a constantly elevated body temperature (37-38 ° C) or its sharp jump to high values.
Treatment of congestive mastitis is the same as for lactostasis. But if the disease has progressed to the next stage, then they take a break from breastfeeding and carry out antibacterial therapy. To maintain lactation, continue to express milk.
Relief of pain during breastfeeding

In breastfeeding, the first months and the end of lactation are considered the most difficult. At this time, unpleasant complications are common. To combat milk stagnation, no special treatment is required, and pain is reduced in various ways.
- More often they give the baby the affected breast and express the remainder. Feeding breaks should be no more than 3 hours.
- Before feeding, warm the breasts with warm, but not hot water, or apply a warm heating pad for 10 minutes. High temperature is dangerous.
- Continue preparation with a light massage. Movements should be smooth; you should not press hard on tight places, so as not to squeeze other ducts.
- Since the baby may not have enough strength to draw out thickened milk, express a small amount of milk with a breast pump before breastfeeding.
- Possible swelling is eliminated by applying cool cabbage leaves, ointment with arnica or Troxevasin.
- If signs of inflammation appear or improvement does not occur after 2-3 days, you should consult a doctor and follow his recommendations.
Throughout the lactation period, a nursing mother must take care of her health and follow the rules of hygiene. The main causes of breast pain can be prevented by wearing comfortable underwear, sleeping on your side or back, regular feeding and expressing leftovers.



